NATO’s Role in Global Security

Nato members – NATO, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, has played a pivotal role in maintaining international peace and stability since its inception in 1949. Its mission has evolved over the years, reflecting changing global security dynamics and challenges.
Initially established as a defensive alliance to counter the threat of Soviet expansion, NATO’s role has expanded to include collective security, crisis management, and cooperative security.
Current Role in Maintaining International Peace and Stability, Nato members
Today, NATO remains a cornerstone of Euro-Atlantic security, providing a framework for cooperation and collective defense among its 30 member states. Its core mission is to deter aggression and ensure the security of its members, based on the principle of collective defense enshrined in Article 5 of the Washington Treaty.
NATO’s presence and engagement extend beyond its member states, with active involvement in peacekeeping and stabilization operations around the world. It has played a significant role in conflict resolution and post-conflict reconstruction in regions such as the Balkans, Afghanistan, and Libya.
NATO members have been grappling with the implications of Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, with some calling for a more robust response. In a recent interview with ABC News , President Biden reiterated his commitment to Article 5 of the NATO treaty, which states that an attack on one member is an attack on all.
He also emphasized the importance of unity among NATO members in the face of Russian aggression.
Challenges and Opportunities in the 21st Century
NATO faces several challenges in the 21st century, including the rise of new threats such as terrorism, cyber warfare, and hybrid warfare. It must adapt its strategies and capabilities to address these evolving threats while maintaining its core mission of collective defense.
NATO members have long been committed to collective security, and President Biden’s recent speech reinforced this commitment. He emphasized the importance of unity and cooperation among NATO members in facing global challenges, such as the ongoing conflict in Ukraine and the rise of authoritarianism.
NATO also faces opportunities to strengthen its partnerships with non-member states and international organizations. By fostering cooperation and dialogue, NATO can enhance its global reach and influence in promoting peace and stability.
Member States and Contributions: Nato Members
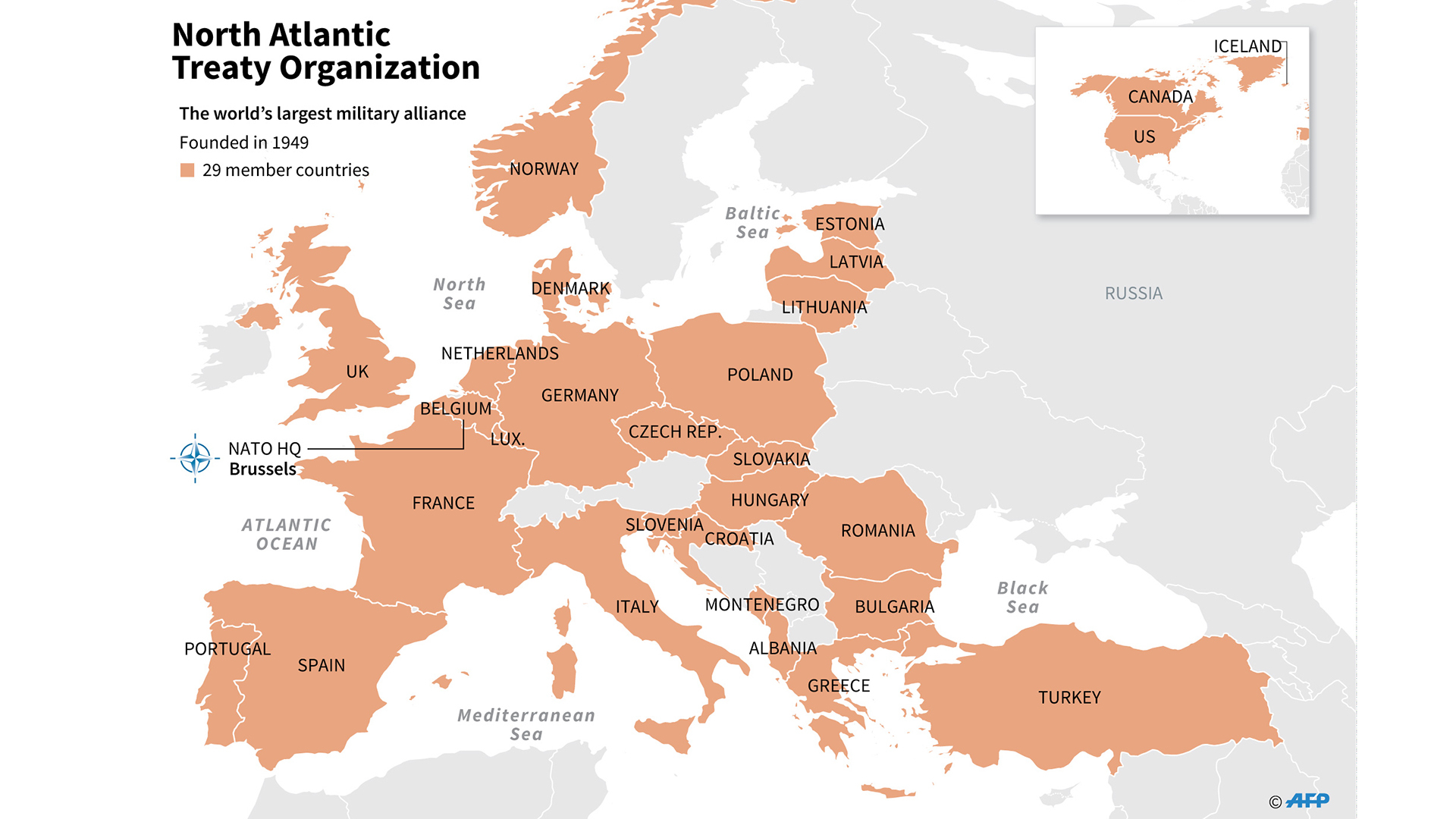
NATO, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization, is an intergovernmental military alliance of 30 member states from North America and Europe. The organization was established in the aftermath of World War II to provide collective security against the Soviet Union and its satellite states.
Each member state contributes to NATO in different ways, both militarily and financially. The most significant military contributions come from the United States, which provides around 70% of NATO’s military spending and personnel. Other major contributors include the United Kingdom, France, Germany, and Italy.
Types of Contributions
- Military contributions: Member states contribute troops, ships, aircraft, and other military assets to NATO. These assets are used for a variety of purposes, including collective defense, peacekeeping, and disaster relief.
- Financial contributions: Member states also contribute financially to NATO. These contributions are used to fund the organization’s operating costs, as well as to purchase new equipment and infrastructure.
- Political contributions: Member states also contribute politically to NATO. They do this by participating in the organization’s decision-making process and by providing diplomatic support for NATO’s missions.
Importance of Burden-Sharing
Burden-sharing is an important principle within NATO. It means that all member states should contribute fairly to the alliance’s collective security. This is important because it ensures that no one country bears too much of the burden of defending the alliance.
There are a number of ways to measure burden-sharing. One common measure is to compare the percentage of GDP that each member state spends on defense. Another measure is to compare the number of troops that each member state contributes to NATO.
The United States has traditionally been the largest contributor to NATO, but in recent years, other member states have begun to increase their contributions. This is a positive development, as it shows that all member states are committed to the alliance’s collective security.
NATO’s Structure and Decision-Making

NATO’s organizational structure is designed to facilitate consultation and decision-making among its member states. The North Atlantic Council (NAC) is the principal political decision-making body within NATO. It comprises permanent representatives from all member states and meets regularly at NATO headquarters in Brussels. The NAC is chaired by the NATO Secretary General and makes decisions on all matters concerning the Alliance, including political and military issues.
The Military Committee (MC) is the senior military authority within NATO. It is composed of the Chiefs of Defense of all member states and meets regularly to provide military advice to the NAC. The MC is chaired by the Chairman of the Military Committee, who is also the Supreme Allied Commander Europe (SACEUR).
Decision-Making Process
NATO’s decision-making process is based on consensus. This means that all decisions must be agreed upon by all member states. In practice, this means that decisions are often the result of extensive negotiation and compromise. The consensus rule can make it difficult to reach decisions quickly, but it also ensures that all member states have a voice in the decision-making process.
Role of Consensus
Consensus is a fundamental principle of NATO’s decision-making process. It ensures that all member states have a say in the decisions that are made and that no single state can dominate the Alliance. Consensus also helps to build trust and cooperation among member states.